By CASC4DE December 12, 2024
At CASC4DE, we are always on the lookout for groundbreaking scientific advancements that resonate with our commitment to quality and sustainability across industries. Recent discoveries have shed light on an innovative way to tackle a pressing environmental issue: forever chemicals, or PFAS (per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances).
🌱 Microbes to the Rescue 🦠
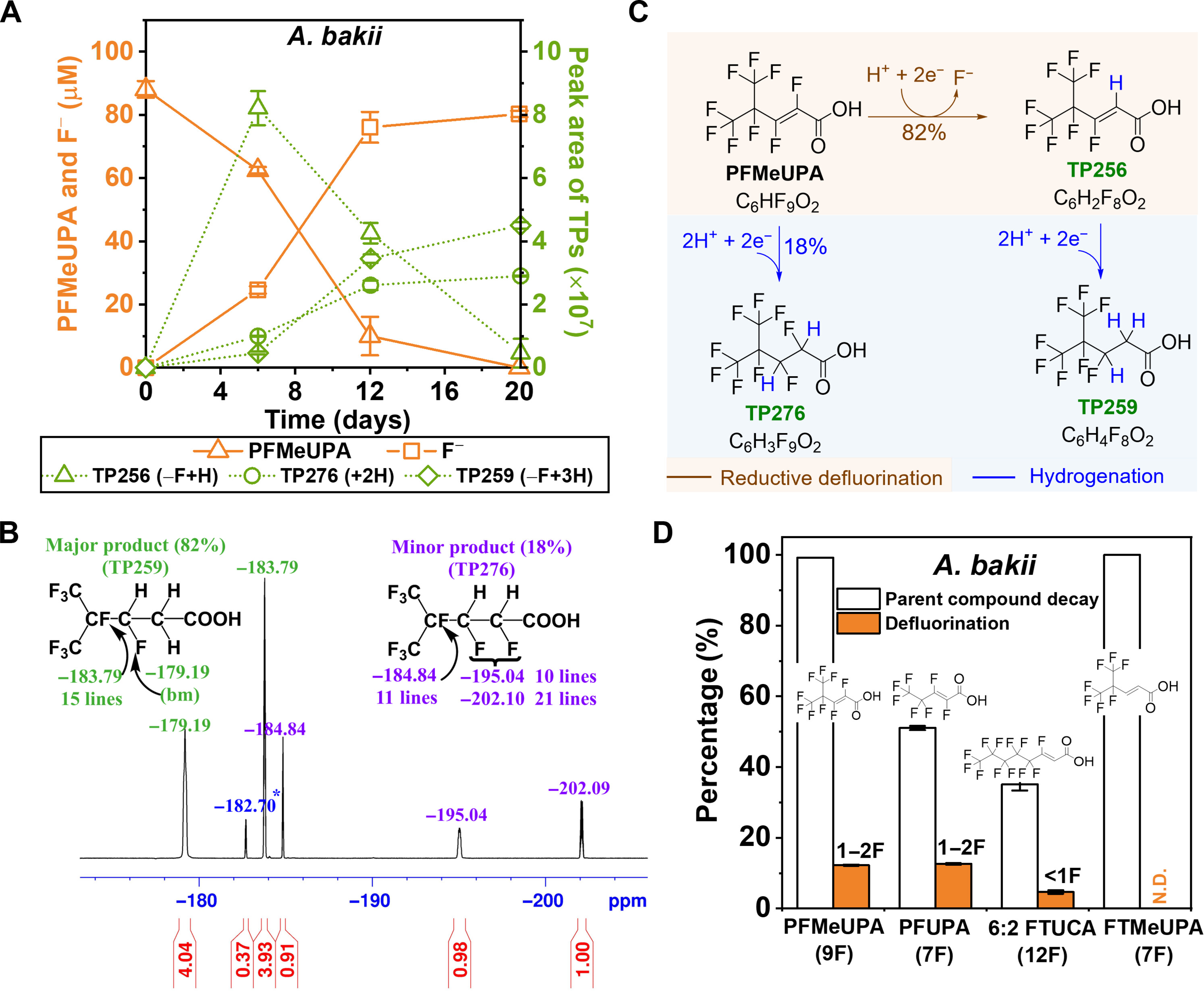
A study published in Science Advances and further detailed by researchers at the University of California, Riverside, has identified Acetobacterium microorganisms capable of naturally breaking down specific unsaturated PFAS compounds. These microbes utilize natural metabolic pathways to break the exceptionally strong carbon-fluorine bonds in PFAS molecules, which are responsible for their notorious persistence in the environment. The researchers focused on a class of PFAS compounds known as perfluoroalkyl carboxylic acids. By providing these microorganisms with PFAS as a carbon source under controlled conditions, the team observed a degradation process previously thought unachievable. Importantly, this microbial activity occurs at normal temperatures and pressures, making it far more sustainable compared to existing methods such as high-temperature incineration or chemical treatments. The biotransformation products were checked by 19F-NMR🧲.
📈 Challenges Ahead
While promising, work remains to extend these findings across broader PFAS structures and environmental conditions. PFAS, often referred to as “forever chemicals,” have become a global environmental concern due to their widespread use and resistance to breakdown. Unlike traditional remediation methods, which are often costly and generate hazardous byproducts, this microbial approach could offer a clean, efficient, and scalable solution for mitigating PFAS contamination. Early tests suggest promising applications for water treatment facilities and industrial waste management systems. The study authors emphasized that this discovery represents just the beginning. Future research will explore how to enhance these microbial processes, potentially expanding their effectiveness to a broader range of PFAS compounds and real-world environmental conditions.
🌟 Implications for Industry and the Environment
The potential applications of this research are vast, particularly for industries we serve at casc4de—cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and agro-food. Key benefits include:
- Reduced contamination risks: Safer processing of materials and minimized exposure to PFAS.
- Enhanced environmental compliance: Companies can meet stricter regulations without relying on energy-intensive methods.
- Sustainable supply chains: Integrating natural remediation methods supports broader ecological goals.
As a company committed to quality and sustainability, casc4de is excited to follow these developments closely. This breakthrough underscores the critical role of science in addressing long-standing environmental challenges, and we are eager to see how these findings translate into actionable solutions.
Illustration credit to the Science Advances publication authors.




